What Best Describes the Major Product of an E1 Reaction
Rate k solvent 28. A SN2 B SN1 C E2 D E1 E there is no way to know 5.

Solved 1 Which Of The Following Terms Best Describes Chegg Com
Given that optically pure R 1-chloro-1-phenylethane has a specific rotation of -1090 and that optically pure R 1-phenyl-1-ethylamine has a specific rotation of 393 which of the following statements best describes this reaction.
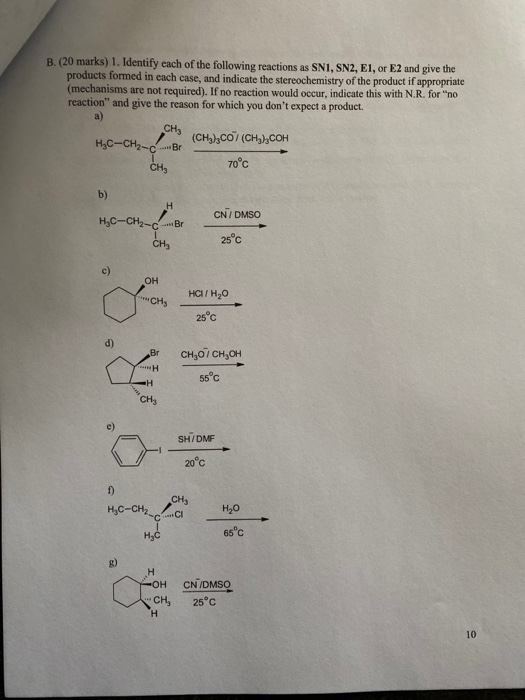
. The reaction is concerted meaning that all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. With E2 reactions there are exceptions see antiperiplanar. Predict the major product of the reaction sequence below.
Istep aSN1 d E2 t-BuOH b SN2 e Multiple POIAY Protic c E1 f None of them ble 12. D The reaction undergoes an E2-type elimination mechanism in conjunction with a methyl shift. Actually primary carbocation formed can either lose a H to form but-1-ene or may undergo rearrangement and shift to.
Which mechanism best describes the chemical process shown below. The MAJOR product of the following reaction conditions will result from. The terms SN1 and E1 mean substitution nucleophilic unimolecular and elimination unimolecular respectively.
Determine a possible structure for an alkene X formula C9H14 on the basis of the following information. Which mechanism does not react by E2. Identify ALL possible elimination and substitution products that can be formed from the given reagents.
11 A E1 S N2 B E2 S N2 C E1 S N1 D E2 S N1. D The reaction undergoes an E2-type elimination mechanism in conjunction with a methyl shift. The major substitution product of the reaction is 1-phenyl-1-ethylamine with an α25D of -86.
Some more examples of E1 reactions in the dehydration reactions of alcohols. Alkene A Alkene B Alkene C Question 5 As weve seen SN1E1 reactions can be quite messy and can generate multiple products. E1 reaction always follow Zaitsevs rule.
618 100 Dehydration of 1-butanol with concentrated sulfuric acid at 140 C results in the formation of mainly trans-2-butene. Given the following substitution reaction what would the effect be of changing the solvent from CH 3 OH to CH 3 2 SO DMSO. C The reaction undergoes an E1-type elimination mechanism in conjunction with a hydride shift.
X adds one mole of hydrogen on catalytic hydrogenation. They often occur simultaneously and competitively with one another under the same reaction conditions. A The reaction undergoes an E2-type elimination mechanism.
12 Identify the mechanistic pathways respectively for the products in the following reaction. Ii Butan-1-ol upon acid dehydration will give but -2-ene as the major product along with but -1-ene as the minor product. This reaction occurs via a n _____ mechanism.
34 Which of the following statements is false about the E1 reaction. There are 5. Predict the major product when each of the following alcohols is treated with H 2 SO 4.
What is the major product for the following reaction sequence. Which of the following rate laws describes the kinetics of an S N 2 reaction. 11 Identify the mechanistic pathways respectively for the products in the following reaction.
B The reaction follows a new mechanism involving the formation of a carbanion intermediate. 12 A E2 S N1 B E2 S N2 C E1 S N2 D E1 S N1. Beta-Hydrogen is absent.
B The reaction follows a new mechanism involving the formation of a carbanion intermediate. For a simplified model well take B to be a base and LG to be a halogen leaving group. An E1 reaction involves the deprotonation of a hydrogen nearby usually one carbon away or the beta position the carbocation resulting in the formation of an alkene product.
On treatment with hot basic KMnO4 followed by acidification X yields the following dicarboxylic acid. The major product of an elimination reaction is the more substituted alkene. Rate k alkyl halide nucleophile D.
Consider the reaction shown below in order to answer questions 5-6. Chemistry questions and answers. Which mechanism best describes the chemical process shown below.
Which of the following best describes the major product s of the following reaction s. An alkyl halide reacts with a strong base to form an alkene. 13 What is the major product in the following.
Rate k nucleophile C. A The reaction undergoes an E2-type elimination mechanism. Science Chemistry QA Library 11 Which mechanism best describes the pathway of the following reaction.
A B C D E 4. C The reaction undergoes an E1-type elimination mechanism in conjunction with a hydride shift. The answers can be found under the Dehydration of Alcohols by E1 and E2 Elimination with Practice Problems post.
A The rate determining step is always the first step in the mechanism b The mechanism always forms at least one intermediate c The most substituted alkene is the major E1 product d Carbocation rearrangements can occur in this mechanism e Loss of a leaving group is always one of the. NaNH2 excess mineral oil heat 1b. OH H2SO4 A the alkene double bond is conjugated the alkene double bond is terminal the alkene double bond is E configuration the alkene double bond is configuration the alkene double bond is neither E nor Z the alkene.
The product of the reaction is a n _____. When more than one alkene product is possible the major product will be the more substituted alkene. It states that in a regioselective E1 or E2 reaction the major product is the more stable alkene ie the alkene with the more highly substituted double bond.
Draw a suitable mechanism for each transformation. In elimination reactions the most highly substituted alkene product is the major product. These two reaction types are being considered together for two reasons.
Rate k alkyl halide B. Choose all that apply. In order to accomplish this a base is required.
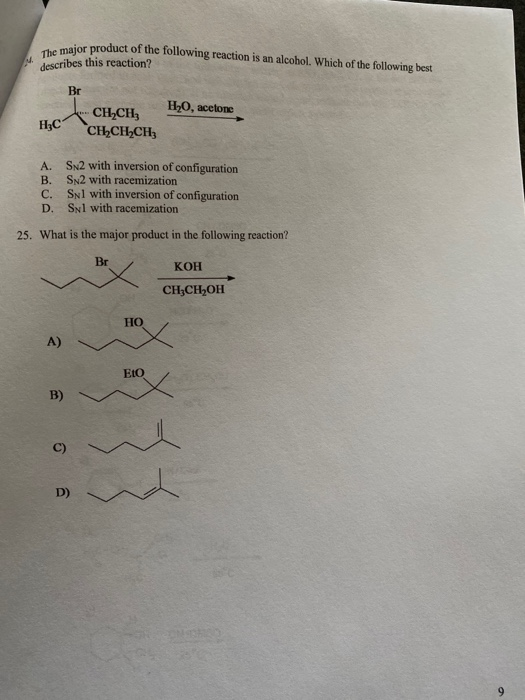
Solved The Major Product Maior Product Of The Following Chegg Com

Solved Which Term Below Best Describes The Mechanism Of The Chegg Com

Solved The Major Product Maior Product Of The Following Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment